Introduction
In the current digital landscape, cybersecurity risks are still developing at a startling rate. While organizations invest heavily in firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and endpoint protection, one of the most dangerous vulnerabilities often lies within their own walls: insider threats. Unlike external hackers, insider threats are perpetrated by individuals who already have legitimate access to the organization’s systems and data. Detecting these threats requires a different approach – and that’s where behavior analytics comes into play.
Definition
The process of gathering, examining, and interpreting information on the actions of users or entities in order to spot trends, patterns, and abnormalities is known as behaviour analytics. It focuses on understanding how individuals or systems interact within a network, application, or environment to detect suspicious activities, improve security, enhance user experience, and support decision-making. This approach is widely used in cybersecurity, marketing, and business intelligence to predict behavior and prevent risks.
What Are Insider Threats?
Insider threats occur when employees, contractors, or trusted partners misuse their access to an organization’s systems or data. These threats can be malicious, where the insider acts with intent to harm (e.g., stealing sensitive data for financial gain or revenge), or negligent, where the insider unintentionally causes harm (e.g., clicking on phishing emails or mishandling data).
According to the 2023 Cost of Insider Threats Report, the average cost of an insider-related incident exceeds $15 million, and the number of incidents continues to rise annually. Traditional security solutions often fail to detect such threats because insiders operate within the bounds of their granted privileges, making their actions appear legitimate – at least on the surface.
This is where User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) or simply behavior analytics comes in, offering a proactive way to spot abnormal patterns that could indicate malicious or negligent behavior.
What is Behavior Analytics in Cybersecurity?
Behavior analytics involves collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data related to user activities and system interactions to establish a baseline of normal behavior. This baseline can then be used to identify deviations that may indicate suspicious activity.
For example, if an employee typically logs in between 9 AM and 5 PM from a corporate laptop in the office, but suddenly accesses sensitive data at 2 AM from a remote location, the system flags this as an anomaly.
Behavior analytics leverages machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) to detect subtle patterns that may go unnoticed by traditional rule-based systems. Unlike static security policies, behavior analytics adapts over time as user behavior changes, making it a dynamic and intelligent security layer.
Why Traditional Security Measures Fall Short
Firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems are essential, but they are designed to combat external threats. Insider threats often bypass these measures because insiders are trusted users with legitimate access.
Here are key reasons why traditional tools struggle with insider threats:
- Legitimate Credentials: Insiders use their own credentials, so logins and access may not trigger alerts.
- Context Blindness: Traditional systems don’t analyze behavioral context; they rely on static rules.
- Delayed Detection: Most systems detect breaches after data has been exfiltrated, not before.
Behavior analytics fills this gap by continuously monitoring and learning from user behavior, enabling real-time anomaly detection.
How Behavior Analytics Identifies Insider Threats
Behavior analytics tools use advanced algorithms to monitor activities across multiple data sources, including network logs, application logs, endpoint data, and identity systems. Here’s how it works:
Baseline Creation:
The system collects historical data on each user’s behavior, such as login times, file access patterns, device usage, and network activity. Over time, it creates a baseline of what “normal” looks like for that user.
Continuous Monitoring:
After establishing a baseline, the system monitors user activity in real-time. Every action is scored against the baseline to determine whether it’s normal or unusual.
Anomaly Detection:
If a user suddenly performs actions that deviate significantly from the baseline – such as downloading large volumes of sensitive files, accessing systems they rarely use, or connecting from unusual geographic locations – the system flags these behaviors.
Risk Scoring:
Behavior analytics doesn’t rely on a single anomaly to trigger an alert. Instead, it assigns risk scores based on the severity and frequency of anomalies. For instance, logging in after hours may not be alarming by itself, but combined with unusual file transfers, it becomes a red flag.
Automated Response and Alerts:
Many advanced solutions integrate with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) platforms, enabling automated alerts, access restrictions, or multi-factor authentication challenges when risky behavior is detected.
Common Insider Threat Scenarios Detected by Behavior Analytics
Data Exfiltration:
An employee preparing to leave the company may copy large amounts of proprietary data to a personal device. Behavior analytics can detect unusual file transfer patterns and prevent data theft.
Privilege Abuse:
A system administrator with elevated permissions might access confidential HR or financial data without a valid business reason. Behavioral monitoring flags these abnormal access patterns.
Compromised Accounts:
When an attacker steals employee credentials through phishing or malware, they often behave differently than the legitimate user. Analytics can detect anomalies such as logging in from a foreign country or performing actions outside the user’s role.
Negligent Behavior:
Employees unintentionally uploading sensitive data to public cloud services or clicking on suspicious links can expose the organization to risk. Behavior analytics helps detect and mitigate these actions before they escalate.
Benefits of Using Behavior Analytics for Insider Threat Detection
- Early Detection: Identifies risks before data is stolen or systems are compromised.
- Reduced False Positives: Unlike static rules, behavior analytics focuses on patterns and context, reducing noise.
- Adaptive Security: Learns and evolves with changing user behavior.
- Compliance and Forensics: Provides detailed audit trails for investigations and regulatory requirements.
Challenges and Best Practices
While behavior analytics is powerful, organizations should consider the following challenges and best practices:
Challenges
- Data Privacy Concerns: Monitoring user behavior can raise privacy issues if not handled transparently.
- Integration Complexity: Deploying behavior analytics requires integration with existing systems.
- False Negatives: Sophisticated insiders may mimic normal behavior to avoid detection.
Best Practices
- Communicate Transparency: Inform employees about monitoring for security purposes.
- Start Small: Begin with critical systems and gradually expand coverage.
- Combine with Zero Trust: Behavior analytics works best as part of a broader Zero Trust architecture.
- Regularly Update Models: Ensure ML models are retrained to reflect current behavior trends.
The Future of Behavior Analytics in Cybersecurity
As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, AI-driven behavior analytics will play an increasingly critical role in enterprise security strategies. Future advancements may include:
- Deeper Contextual Awareness: Combining behavioral data with environmental factors like device health and network conditions.
- Predictive Analytics: Moving from reactive detection to predicting potential insider threats before they happen.
- Integration with SOAR: Automated incident response systems that act in real time based on behavior analytics.
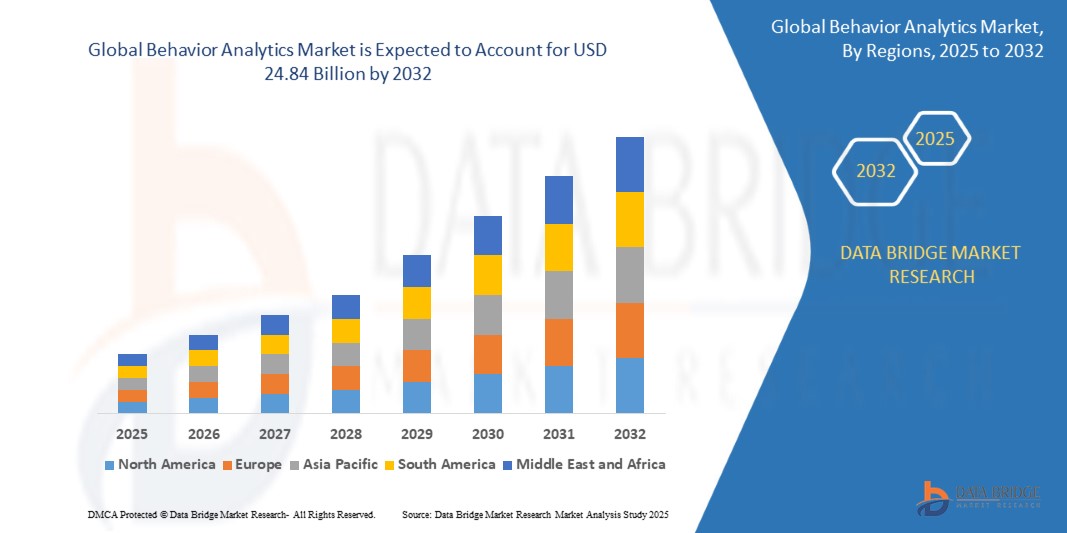
Growth Rate of Behavior Analytics Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the global behavior analytics market was valued at USD 4.82 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 24.84 billion by 2032, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22.75%.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-behavior-analytics-market
Conclusion
One of the most challenging issues in cybersecurity is dealing with insider attacks. Traditional defenses alone are not enough because insiders operate under the guise of trust and legitimate access. Behavior analytics provides a powerful, adaptive approach to detecting these threats in real-time by identifying anomalies in user behavior.